Check If a String Is a Valid Sequence from Root to Leaves Path in a Binary Tree
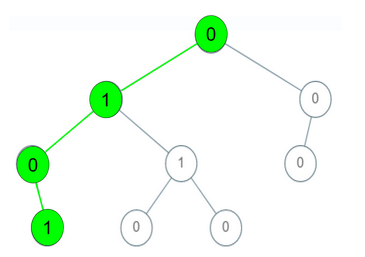
Given a binary tree where each path going from the root to any leaf form a valid sequence , check if a given string is a valid sequence in such binary tree. We get the given string from the concatenation of an array of integers arr and the concatenation of all values of the nodes along a path results in a sequence in the given binary tree. Example 1: Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,0,1] Output: true Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 is a valid sequence (green color in the figure). Other valid sequences are: 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 0 -> 0 -> 0 Example 2: Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,0,1] Output: false Explanation: The path 0 -> 0 -> 1 does not exist, therefore it is not even a sequence. Example 3: Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,1] Output: false Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 1 is a seq...